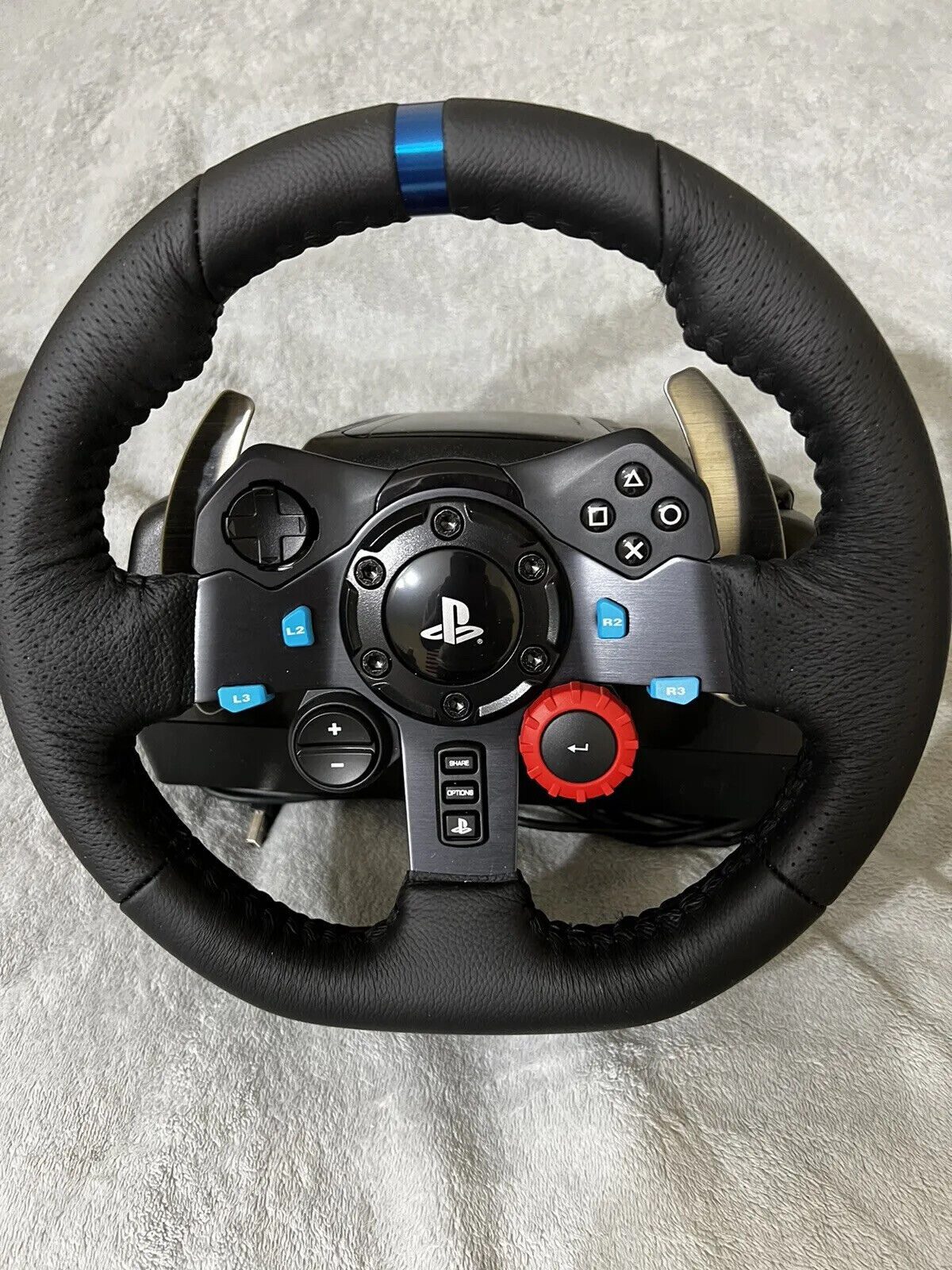
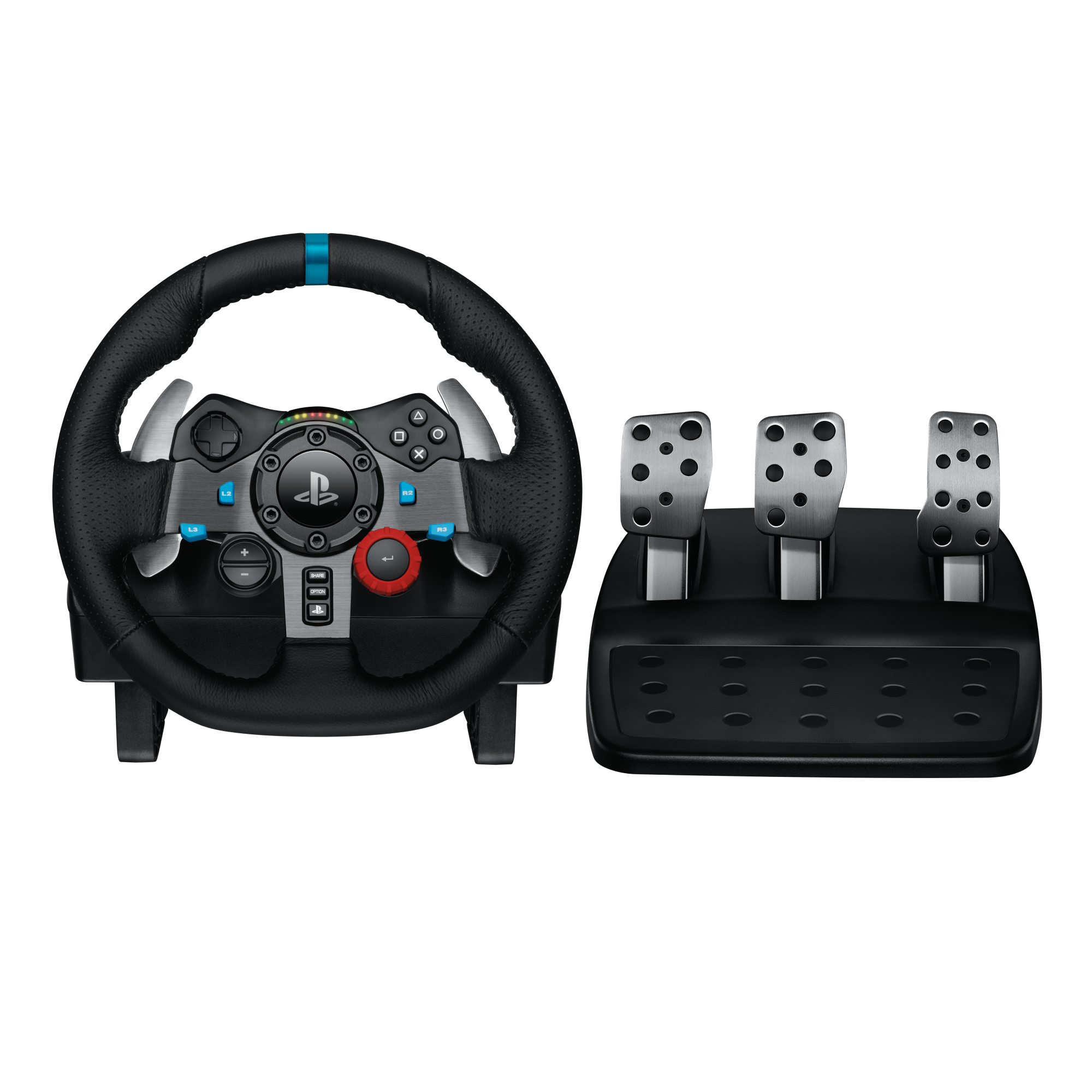
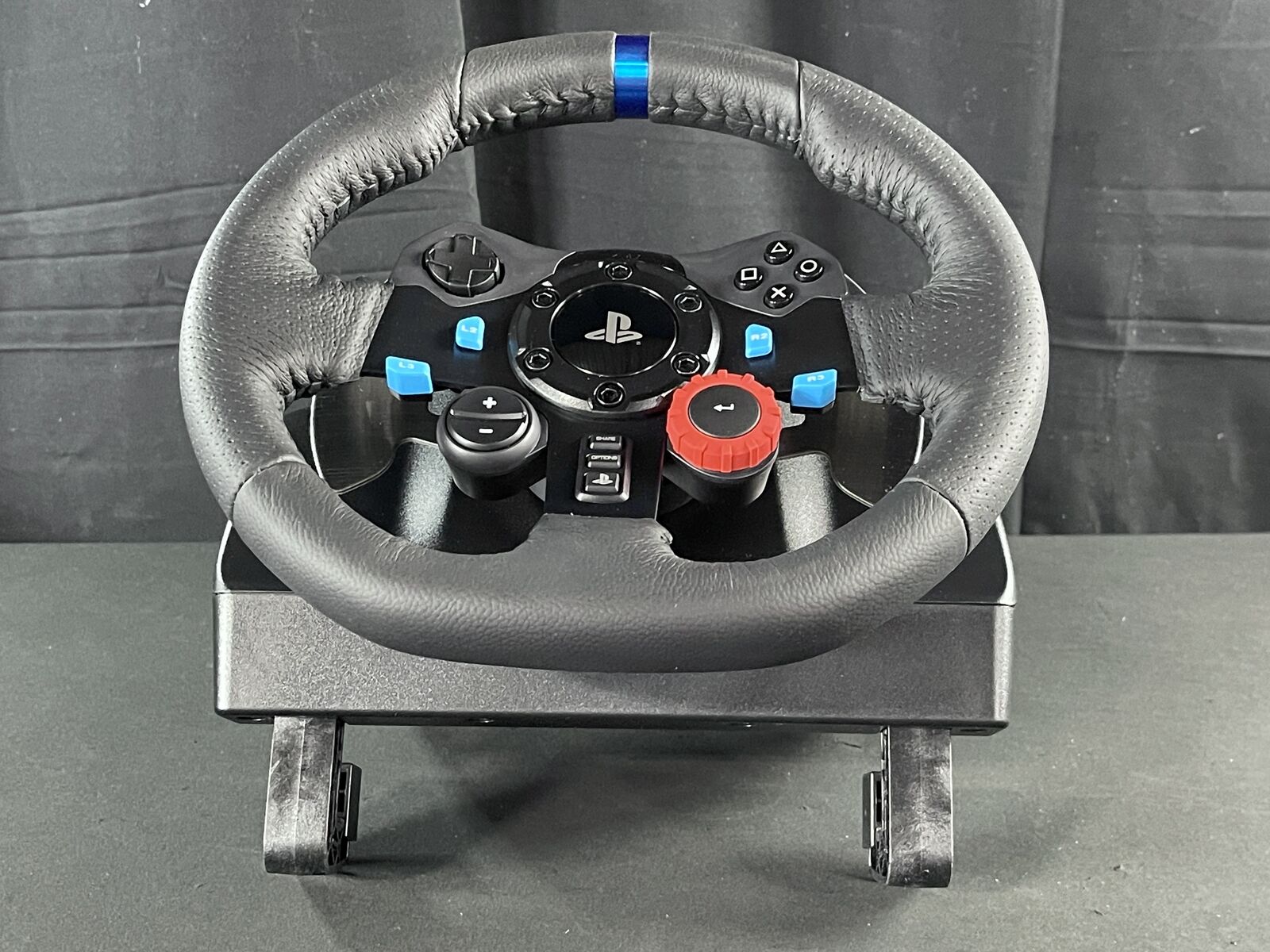
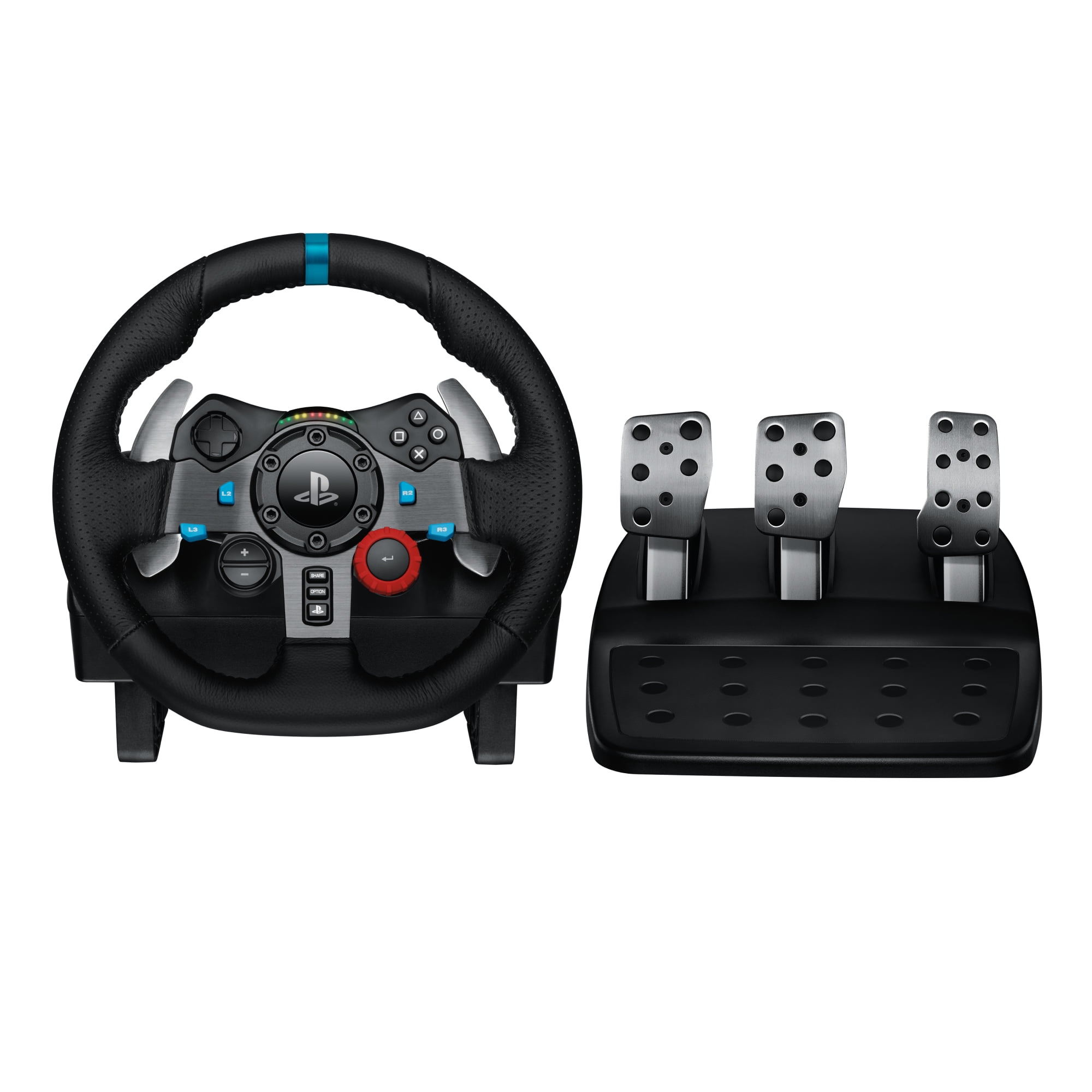
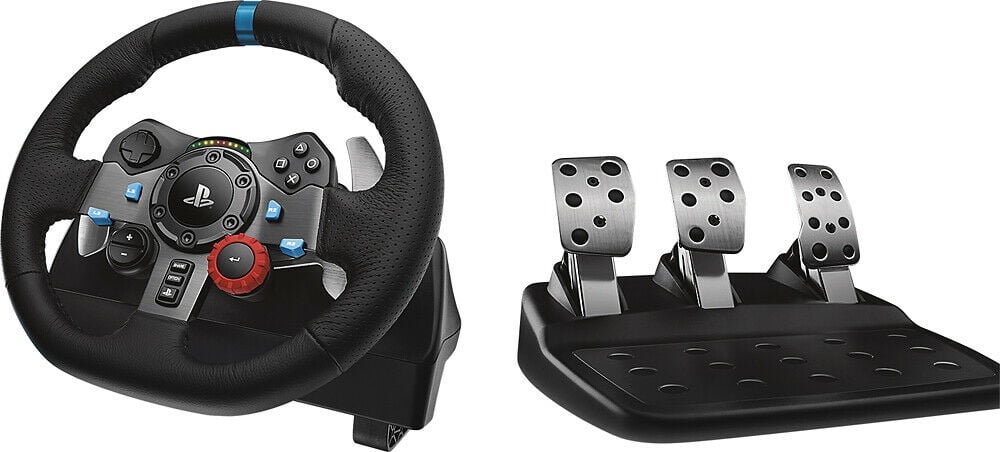
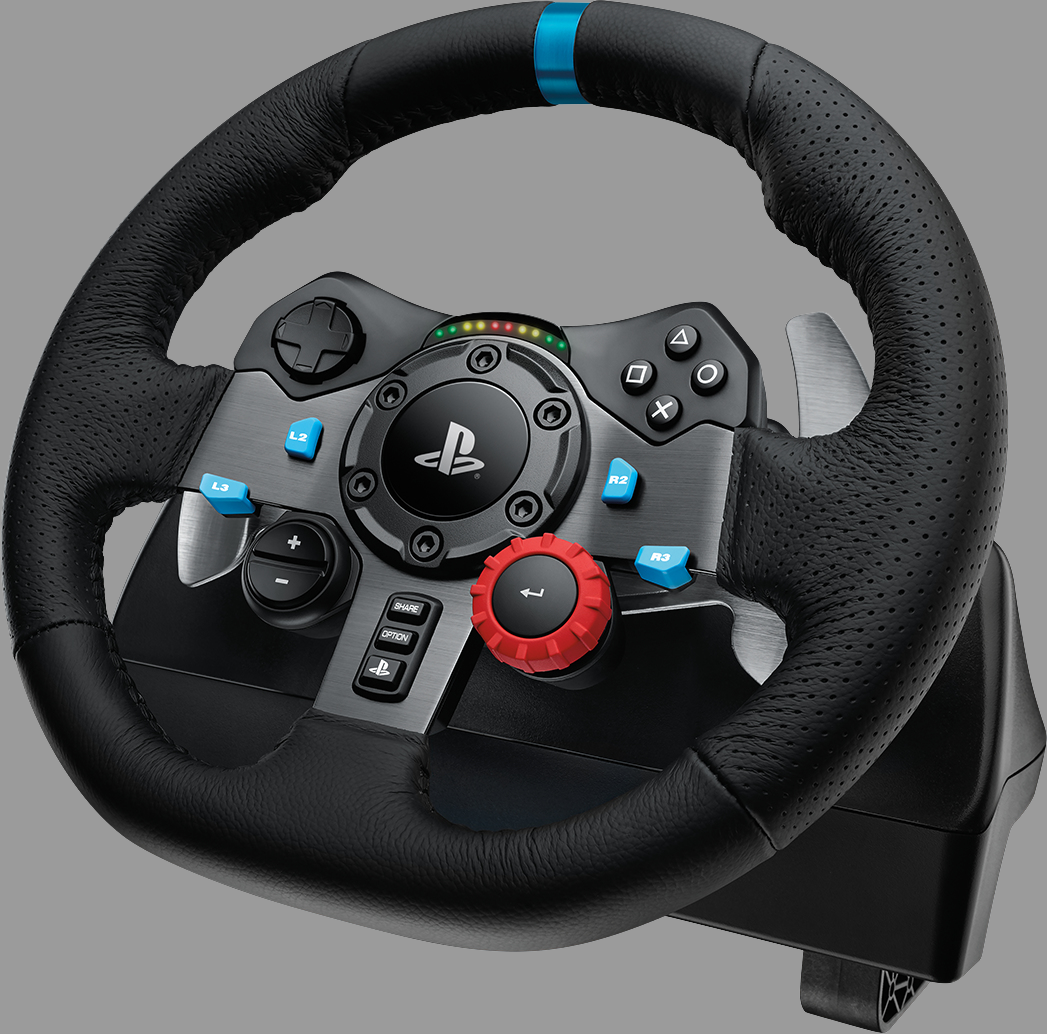
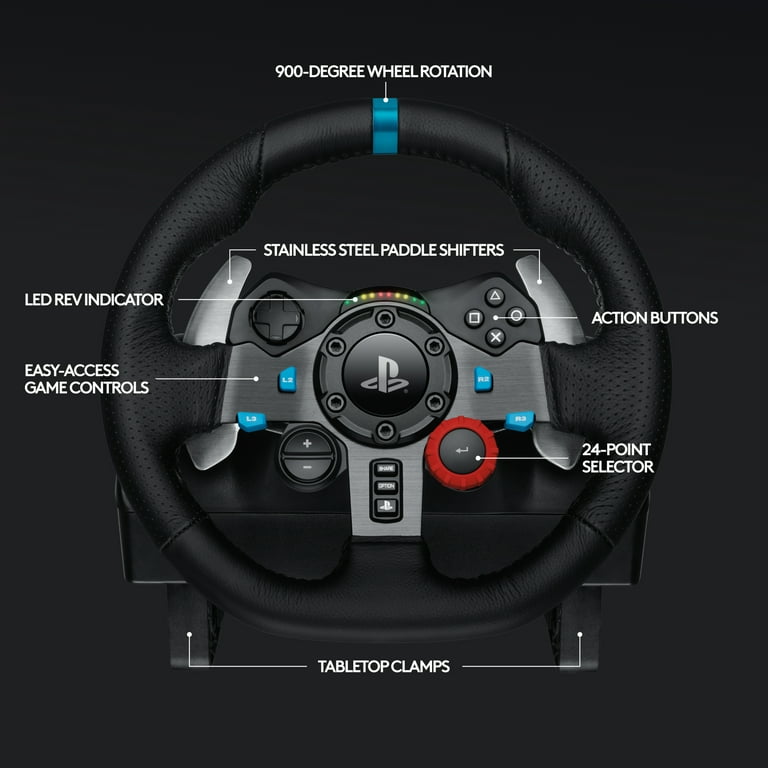
Amazon.com: Logitech G29 Driving Force Racing Wheel and Floor Pedals, Real Force Feedback, Stainless Steel Paddle Shifters, Leather Steering Wheel Cover, Adjustable Floor Pedals, EU-Plug, PS4/PS3/PC/Mac, Black : Video Games

Amazon.com: Logitech G29 Driving Force Racing Wheel and Floor Pedals, Real Force Feedback, Stainless Steel Paddle Shifters, Leather Steering Wheel Cover for PS5, PS4, PC, Mac - Black

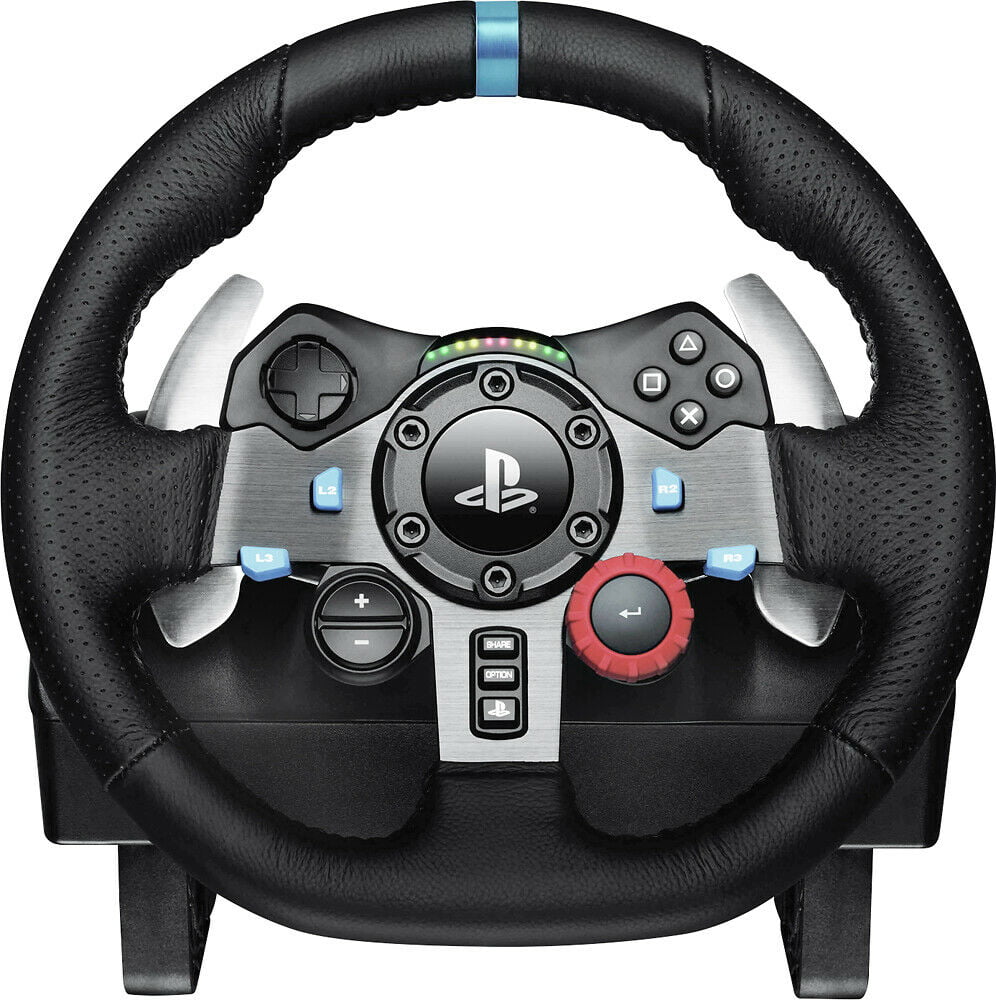
original logitech g29 Driving force racing wheel for game ps4 ps3 ps5 wholesale gaming steering wheel

Logitech G29 Driving Force Racing Wheel and Floor Pedals for PS5, PS4, PC, Mac Black 941-000110 - Best Buy

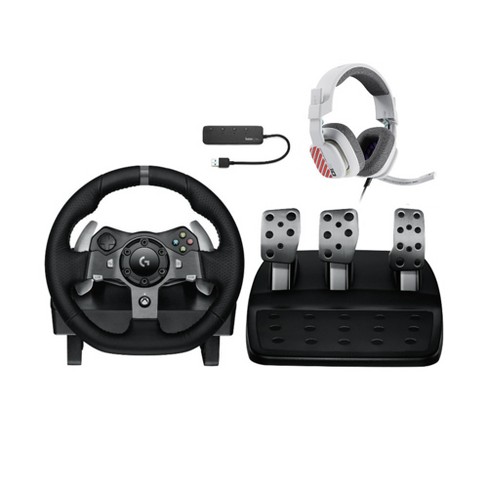
Amazon.com: Logitech G29 Driving Force Racing Wheel + Floor Pedals + G Driving Force Shifter Bundle - PS5/PS4/PC : Everything Else